
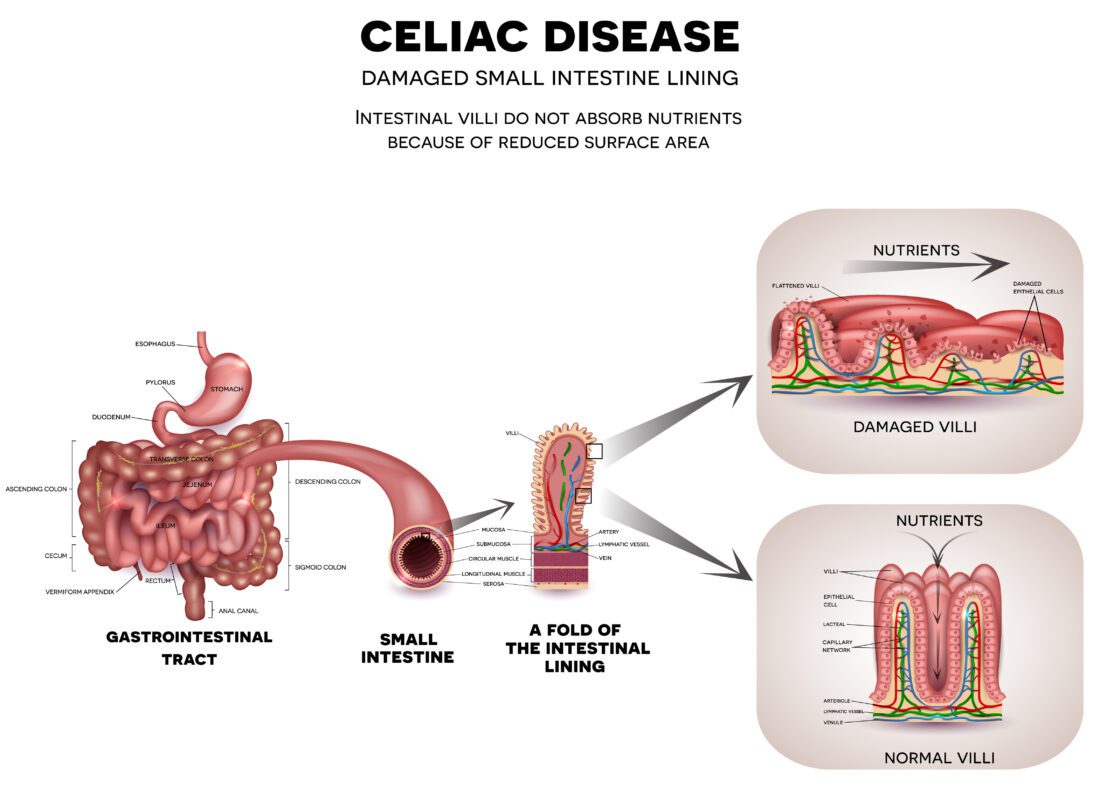
Why do you think so many people around you are going gluten-free? One of the most prevalent causes is celiac disease. It’s a multifactorial gastrointestinal disorder triggered by an autoimmune reaction to gluten.
Just for the sake of introduction, ‘gluten’ refers to the proteins found in barley, wheat, rye and their hybrids. As for the immune reaction, it is responsible for causing damage to hairlike projections, also known as the ‘villi’ that lines the small intestine. Destroying those is sure to have health consequences, whereby malnutrition, infertility and damage to small bowel are a few to name. After all, those are responsible for absorbing minerals, vitamins and other nutrients from food. Naturally, with their damage, the nutrient intake dips below the standard, causing complications like cancer, malnutrition and lactose intolerance to develop.
Given the gravity of the situation, it makes absolute sense to know more about celiac disease. We have put together its probable causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods and treatments for you to draw insights.
Celiac patients experience signs and symptoms which may or may not be related to digestive disorders. Adults suffering from this disease complain of the following:
• Diarrhoea
• Bloating and gas
• Nausea and vomiting
• Fatigue
• Abdominal pain
• Constipation
As discussed earlier, adults could also experience non-intestinal signs and symptoms. Any of the following could apply:
• Mouth ulcers
• Anaemia
• Headaches and fatigue
• Joint pain
• Osteoporosis or loss of bone density
• Hyposplenism or reduced functioning of the spleen
On the other hand, children suffering from celiac disease undergo chronic diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting. Swollen belly, gas and foul-smelling stool are other digestive problems encountered by them. Over time, they grow irritable, suffer damage to their tooth enamel, develop short stature, fail to thrive as adults and are more anaemic.
Diagnosing such a disease can be challenging as it shares symptoms with other conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), pancreatic insufficiency, Crohn’s disease and lactose intolerance. However, when a gastroenterologist is approached, the physician looks through medical histories and prescribes tests, like biopsies, blood tests and genetic tests.
Currently, the sole way to treat celiac disease is to curb gluten in the diet. Avoiding food items rich in gluten such as rye, wheat, bread, barley and beer for lifelong can help tackle the disease and heal the intestine. However, ensure you adhere to this treatment method as long as you have been screened for celiac.
Apart from the discussed treatment, the intake of vitamin and mineral supplements helps address deficiencies. So, you could try it and keep your fingers crossed for drug therapies on which researchers are perpetually working to lower the burden of living with celiac disease.
Do you think someone you know is silently suffering from celiac disease? Share this article with that person and spread awareness about this serious autoimmune disease.

Experiencing persistent discomfort in your upper abdomen, accompanied by bloating, gas,
read more
Kidney Failure: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment As reported by the Indian Express in
read more
What actually is Ulcerative Colitis? It is a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, (along w
read more