
Do you often complain of bloating and diarrhoea? Have discomforts and pain in your abdomen become commonplace? Chances are you are suffering from colitis. It is the inflammation of your large intestine or colon, as many people recognise. However, understanding if it is colitis for real requires understanding its various types, symptoms, causes and treatment. So, without further ado, let’s begin.
Colitis is of various types and is provoked due to many causes. While it’s easy to treat some, for instance, those occurring from a bacterial infection like food poisoning, others are serious and take a lot of time to go away. Beware of the severe cases! They may pose a threat to your colon and affect your quality of life. Let us take a look at each of them and examine their causes.
PC is triggered when the C. difficile overgrows and the ‘good’ bacteria fails to balance it. Consequently, C. diff takes over, releases toxins and causes inflammation.
It is mostly people aged 50 and above, smokers and those who have suffered from an autoimmune disease who are diagnosed with microscopic colitis. The medical condition causes abdominal bloating, pain and chronic watery diarrhoea.
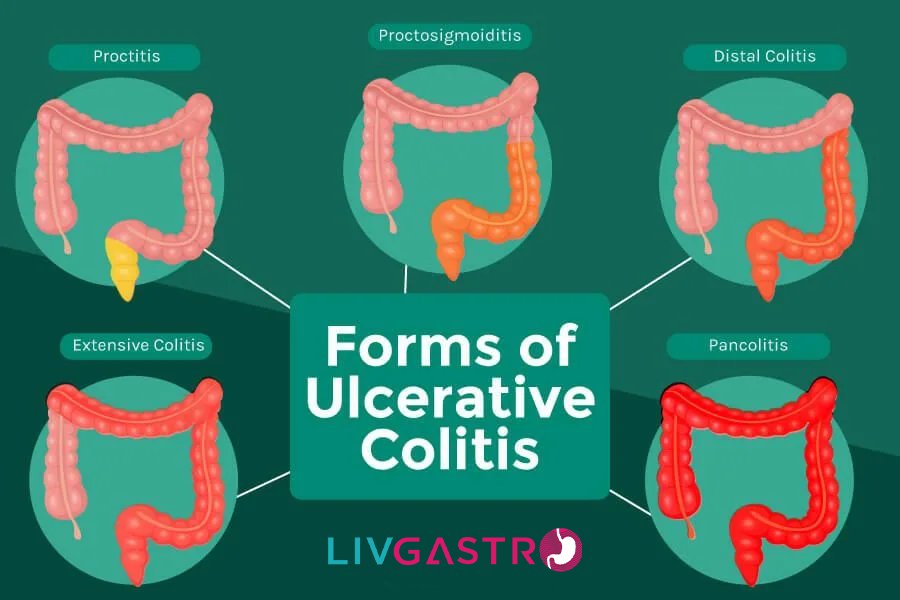
It is the most common type of colitis, where patients have to put up with bleeding ulcers and inflammation. The disease occurs in the rectum but gradually spreads to the colon. UC happens when the bacteria in the digestive tract causes the immune system to overreact.
It is usually blood clots that trigger IC. As the blood flow is cut off to the colon, blockage occurs. The condition recurs when fatty deposits build up in blood vessels. People having underlying conditions like diabetes, trauma or injury, blockage, colon cancer and a history of dehydration and heart failure develop IC more often.
It can be any of the following:
• Fever and chills
• Abdominal pain
• Diarrhoea
• Bloating in the abdomen
• Vomiting
• Unexpected weight loss
• Presence of blood in stool
When you visit a doctor, the physician may enquire about the frequency of symptoms and when they first occurred followed by a thorough physical examination. The medical practitioner may also prescribe diagnostic tests and a few to name would be –
• Ultrasound
• Stool samples
• Colonoscopy
• Abdominal imaging like CT scans or MRI
• Sigmoidoscopy
• Barium enema or an X-ray of the colon
The treatment of this medical condition depends a lot on the type and causes. It mostly includes:
• Diet – A wholesome diet low in fibre and easy to digest cures acute colitis. Avoiding certain foods that cause colitis flare-ups is also a great way to tackle the medical condition.
• Surgery – Surgery is prescribed to people diagnosed with IBD, necrotising enterocolitis and ischemic colitis. However, it may or may not cure the conditions. It can only stop bleeding, remove a blockage or repair a perforation.
• Medications – Medications like immune system suppressors, antibiotics, antidiarrheal drugs, pain killers and antispasmodic drugs can help manage colitis symptoms.
Detection is critical for recovery from colitis. Early diagnosis can curb serious complications. Therefore, whenever you are not feeling well and believe it has something to do with your stomach, talk to a doctor.
Thyroid Disease Diagnosis & Treatment: How is Done? Every organ in the human body has
read more
Overview: Pain is the most common symptom of gallbladder problems, and this sign is mostl
read more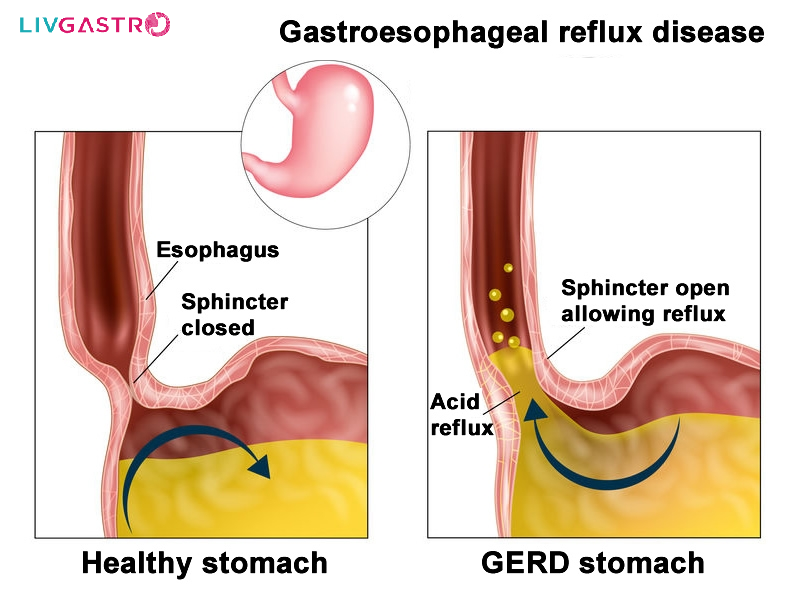
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Causes, Risk Factors, Symptoms & Complications Recurre
read more