
Clinically speaking, gallstones are not stones such as rocks or minerals but stone-like hard deposits made of cholesterol, calcium salt or bilirubin that are often found within the gallbladder which is a small organ that stores bile. However, these stone-like substances may vary in volume – as tiny as a grain of salt or as large as an apricot. To be precise, certain components in bile often crystallize and harden, thus forming gallstones. According to Harvard Health Publications, 80% of gallstones are made of cholesterol, while the remaining 20% consist of calcium salts and bilirubin that are known as Pigment Stones.
As earlier said, gallstones are mostly made of cholesterol as also a few other substances that are outlined below.
Cholesterol Stones: Gallstones often form within the gallbladder when the liver tends to secrete excessive amount of cholesterol in the bile that it cannot break or dissolve and as a result hard stone-like substances develop in course of time.
Bilirubin originated Stones: Bilirubin is a byproduct that is formed while the liver routinely breaks down old red blood cells. However, due to certain disease condition such as cirrhosis of liver as well as a few blood disorders, the liver tends to produce more bilirubin than what is good for the body. Hard substances resembling stones form when the gallbladder fails to break down the excess bilirubin. These are often termed as Pigmented Stones.
According to American College of gastroenterology, 80% of people having gallstone do not have any symptom at all and so are known as Silent Gallstones. However, others have symptoms that include pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. The pain may extend to the right shoulder or the shoulder blade. Besides, gallstone also has the following symptoms:
Excessive and unbearable gallstone/gallbladder pain is medically termed as Gallbladder Attack. In most cases, this may last up to 2 or more hours. However, the gallstones are not actually responsible for the excruciating pain. It happens when the gallstones tend to arrest the movement of the bile from the gallbladder. Nevertheless, the ‘attack’ is preceded by the following three stages that are easy to trail.
Stage-I: Gallstones form within the gallbladder. It is a painless stage.
Stage-II: Gallbladder pain gradually develops but does not continue for long hours. However, the condition exacerbates with consumption of fatty and fried food, while sundry symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea and indigestion appear on the scene.
Stage-III: Medical emergency! Gallstones block the duct while bile moves from the gallbladder. Symptoms include severe stomach/back pain, high temperature and chills.
Apart from physical examination such as checking the color of the skin and the eyes, the attending physician will also ask for diagnostic tests that include:
Ultrasound that provides the most convincing proof of gallstone/gallstones within the gallbladder.
Abdominal CT scan will provide picture of the patient’s liver and surrounding areas.
Gallbladder Radionuclide Scan is the most effective diagnostic test for gallstone that takes around an hour to complete. The test involves injection of radioactive substance in the patient’s veins that travels through the blood and reaches the liver and the gallbladder, immediately detecting any infection or blockage in these organs. Blood Tests Will reveal the amount of bilirubin in the blood and so help the process of diagnosis.
Surgery – Among some of the most sure shot methods of treatment for gallstone involves removal of the source, i.e. the gallbladder itself through laparoscopic surgery. However, general anesthesia is required for this surgery, while the surgeon will make three or four incisions on the abdomen. A lighted device will be inserted into the abdomen to locate the gallbladder, while appropriate surgical instruments will be sent through the other incisions to remove the gallbladder.
In most cases, the patient goes home the same day or a day after.
Medication – Drugs that dissolve gallstones caused by cholesterol are an option if surgery is not recommended. These medications may take several years to remove the gallstones.

What is Cirrhosis Liver Cirrhosis or Cirrhosis denotes a disease condition where the li
read more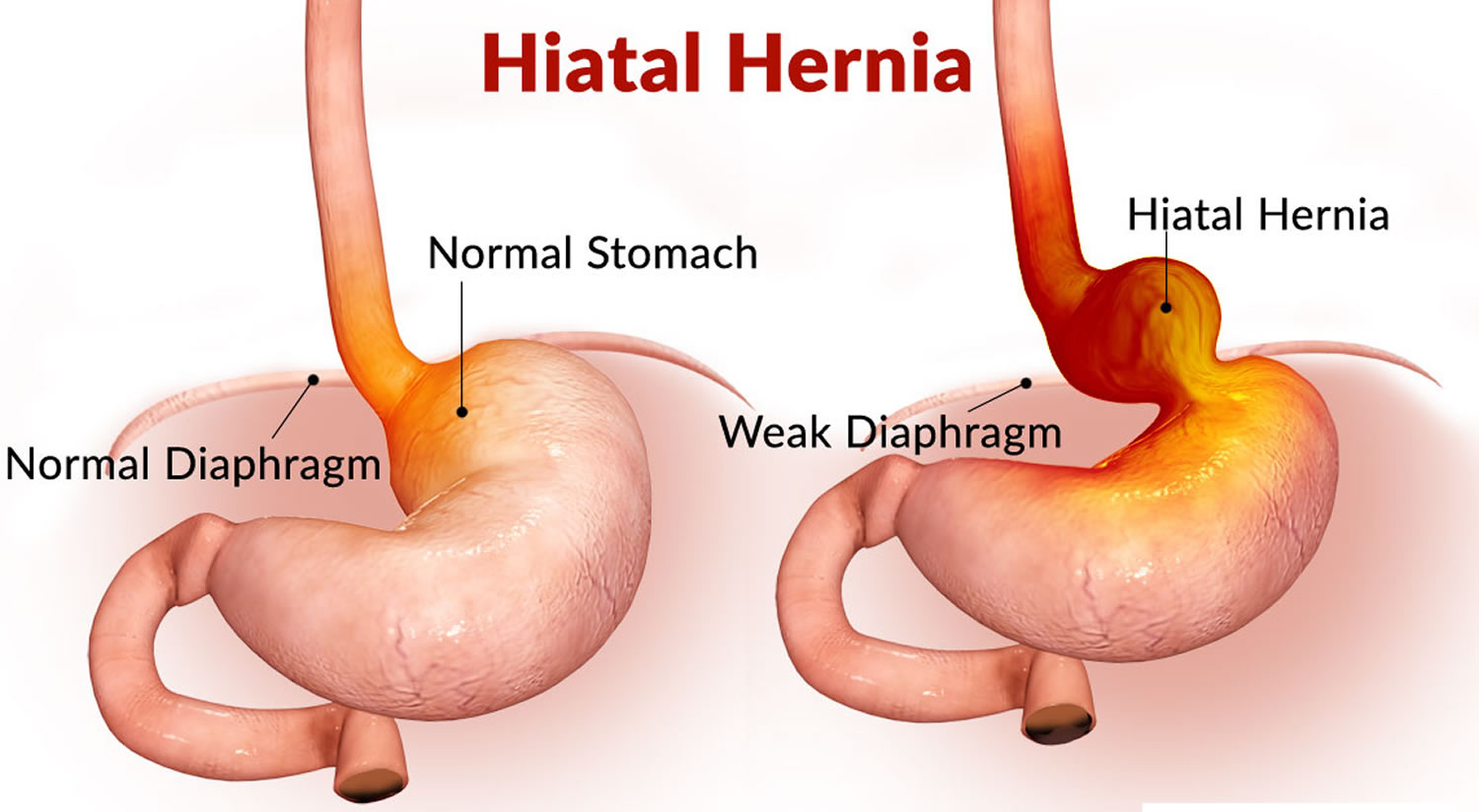
Hiatal Hernia: Understanding its Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment People, mostly those o
read more
Overview The human digestive tract is made up of quite a few organs or parts comprising
read more